Summary: The Gantt chart, invented by Henry Gantt, is used to visualize a timeline in the form of a bar chart. It provides real-time insight into task dependencies, milestones, and the critical path of a project. The prerequisite for a Gantt chart is a work breakdown structure.
What Is a Gantt Chart?
The Gantt chart is named after the system for monitoring work performance invented by Henry Laurence Gantt around 1900. It represents the project schedule of a project using bars along a timeline. This diagram is therefore also called a bar chart or bar schedule. It differs from a timeline diagram in that it also depicts dependencies between tasks. Gantt charts are among the most effective project management methods.
A Gantt chart documents the actual and planned substantive and temporal project progression. It clearly displays the schedule elements – i.e. tasks and milestones – taking into account their relationships, constraints, and dependencies with start date, duration, and end date.
The basis for a Gantt chart is typically a work breakdown structure (WBS). However, the WBS can also be created directly in the Gantt chart as a Work Breakdown Structure. Neither information nor clarity is lost in the process. The tasks in the Gantt chart are derived from the sub-projects, sub-tasks, and work packages of the work breakdown structure.
Gantt Chart Structure: The Most Important Elements at a Glance
Projects: The Time Frame at a Glance
A core feature of the Gantt representation is the ability to arrange elements hierarchically. The top levels contain the projects or sub-projects. These are divided into subordinate activities or products. For example, in a traditional project there are activities for individual phases such as Planning and Implementation. In an agile project, the Gantt chart would be divided into release and sprint activities below the project level.
The expected time frame of a project is determined by the start and end dates of the tasks it contains.
Track project schedules with Allegra
Tasks: Duration, Start and End Date
Activities or tasks group work units such as work packages (tasks, assignments). Tasks must themselves be divisible into sub-tasks to any depth. It is often helpful to use the results (products) arising from these tasks instead of actual tasks and activities. The advantage is that it is easier to verify whether a product is truly complete than to determine whether enough has been done.
Tasks typically have a start date, a duration, and an end date. In some tools, the current work progress is represented by coloring the task bar.
Calculating Duration:
Duration can be calculated in calendar days or working days (business days), depending on how the duration is defined.
- Calendar days: All days are counted, including weekends and holidays.
- Working days: Only business days are counted, i.e. days on which work is actually performed (excluding weekends and holidays).
Duration and Effort: Often Confused
In project management, “duration” and “effort” refer to two different concepts:
-
Duration: Duration refers to the time span needed to complete a specific task or project from start to finish. It indicates how long it takes overall for a task to be completed, regardless of how many resources or workers are involved. For example, a task can have a duration of 5 days, even if only a few hours per day are actually spent working on it.
-
Effort: Effort, on the other hand, describes the amount of work required to complete a task. It is often measured in work hours or work days. Effort takes into account how much labor (e.g. the number of hours an employee works on a task) is required. A task may require 40 hours of effort, regardless of whether these are spread over 5 days or 2 weeks.
In short: Duration refers to the calendar time period, while effort refers to the actual working time that must be invested.
Task Duration and Critical Path
The duration of activities and work packages determines the bar length. Bars of individual tasks may overlap in the Gantt chart. It is advisable to plan buffer times between individual activities.
When tasks affect the project end date and there are no buffer times between them, they are on the critical path. A delay on the critical path always leads to a delay of the project end date. You may already be familiar with this concept from working with network diagrams.
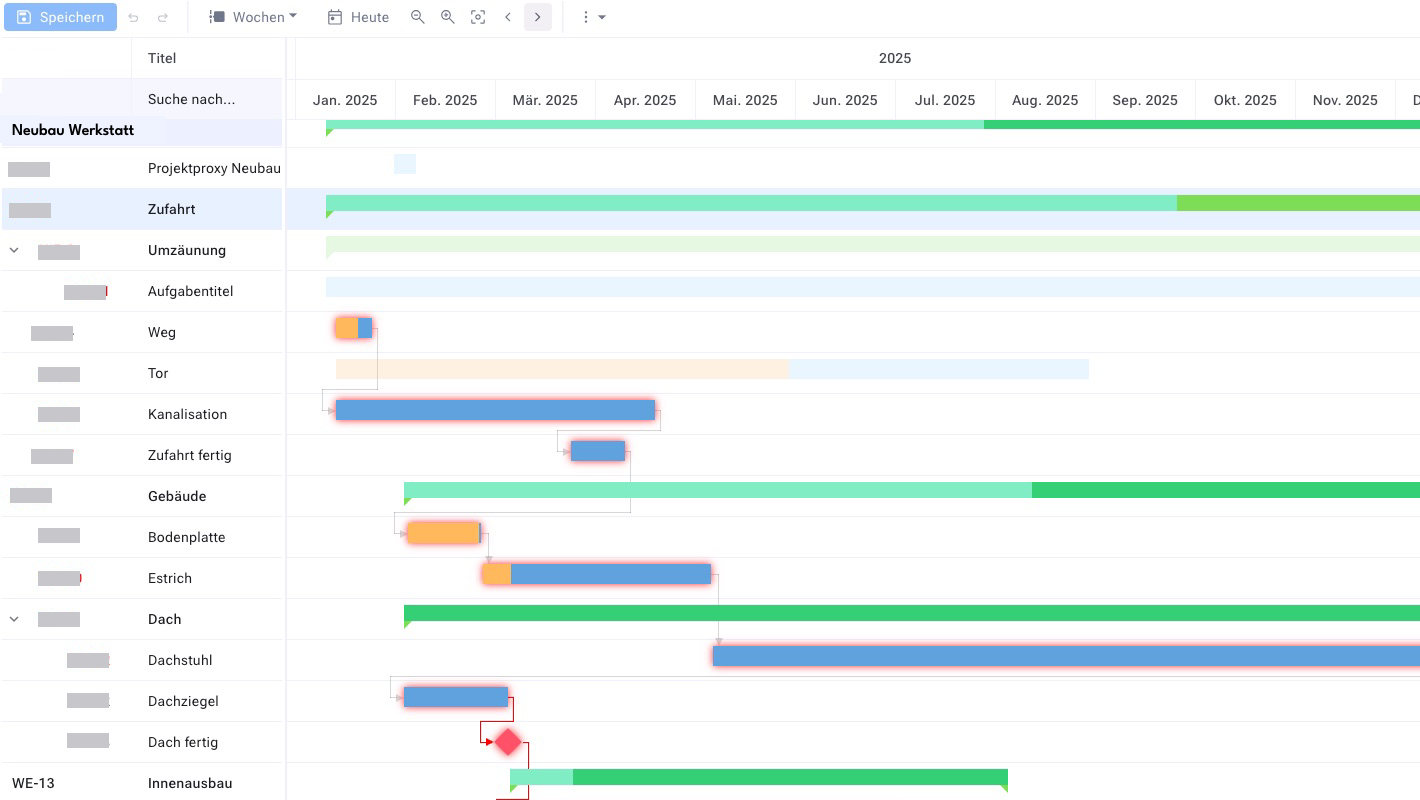
Milestones: The Key Moments in the Project
Milestones mark the completion of a phase or stage in the project. They therefore represent goals that have already been achieved in the project or that are to be pursued. Milestones are indicated by a diamond shape in the Gantt chart. In many tools, tasks with a duration of zero are interpreted as milestones.
In some projects, there are milestones that arise from overarching constraints not controllable by the project, such as a trade fair date. Such milestones must not be moved. Good Gantt tools therefore offer the ability to protect certain tasks and especially milestones from schedule changes.
How to create milestones in the Allegra Gantt chart
Pay Attention to the Critical Path
The duration of activities and work packages determines the bar length. Bars of individual tasks may overlap in the Gantt chart. It is advisable to plan buffer times between individual activities. When tasks affect the project end date and there are no buffer times between them, they are on the critical path. A delay on the critical path always leads to a delay of the project end date. You may already be familiar with this concept from working with network planning techniques.
Note: Planning buffer times contributes significantly to project success. Studies in the field of project management conclude that only 44% of all initiated projects are completed on time. Planning work steps with consideration of buffer times helps to calculate project risks early, estimate project duration realistically, and complete projects on time.
Who Are Gantt Charts Suitable For?
Gantt charts are suitable for a wide range of target groups in project management, especially for those who need a clear, visual representation of tasks, schedules, and dependencies. They are particularly useful for:
-
Project Managers:
- Gantt charts help project managers plan complex projects, monitor progress, and manage resources. They provide an overview of which tasks need to be completed when and what dependencies exist. They are also easily understood by non-experts and can be used as a central management tool in the kick-off meeting and subsequent jour fixe sessions.
-
Project Teams:
- For team members, Gantt charts provide a clear representation of their tasks, deadlines, and dependencies. This helps them better prioritize and coordinate their own work.
-
Stakeholders:
- Stakeholders, such as clients, executives, or investors, benefit from Gantt charts because they provide a clear and visual overview of project progress. They allow them to see at a glance whether the project is on schedule.
-
Resource Planners:
- People responsible for allocating and managing resources (staff, equipment, etc.) can use Gantt charts to plan the deployment of resources over time and identify bottlenecks.
-
Executives:
- For executives, a Gantt chart offers an easy way to stay informed about a project’s status and ensure it stays on track without having to dive into too many details.
Gantt Charts Are Particularly Well-Suited For:
- Medium to large projects: They make it possible to visualize many tasks and dependencies.
- Projects with clearly defined deadlines: When it is important to keep track of deadlines and milestones, Gantt charts are a valuable aid in project controlling.
- Projects with multiple teams or departments: To see how different work packages relate to each other over time.
Gantt Charts Are Less Suitable For:
-
- Very small projects or projects without clear deadlines: Here, the effort of creating a Gantt chart may be greater than the benefit.
- Agile or flexible projects: Agile project management, which relies on rapid adjustments, often prefers other methods such as Kanban boards, as Gantt charts are less flexible in responding to changes.
Advantages of the Gantt Chart
- The Gantt representation is quickly understandable even for non-experts
- The Gantt chart provides a quick overview of project activities
- The duration of activities is easily recognizable by the bar length
- Relationships between activities are easily recognizable through connecting lines
- The current project status is quickly assessable
- Buffer times can be easily identified
- Critical activities or processes can be identified
Dependencies in the Gantt Chart
It is typical for projects that some tasks are dependent on each other. The two main types of dependencies are:
- Dependencies through shared resources
- Logical dependencies
Some tasks can only be started when others are finished, or they depend, for example, on the start of another activity.
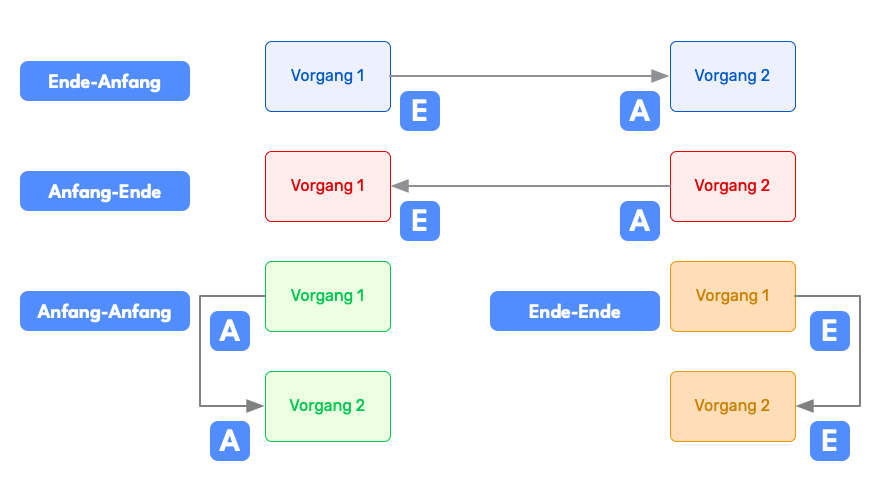
These sequential relationships must be incorporated into the bar chart. The Gantt chart provides four different relationship types for this:
Finish-to-Start
A task can only start when a previous one is finished. This is the most common case. Example: The roof truss can only be erected after the top floor has been bricked and the ceiling of the top floor has been built.
Finish-to-Finish
A task can only end when a previous one is finished. Example: A building acceptance process can only be completed when all other tasks have also been finished. However, it can certainly be started while other tasks are still open.
Start-to-Start
This type of dependency means that the successor task can only begin when the predecessor task has also begun. For example, if you are preparing a table for your guests, you can start preparing the side dish once you have put the main course in the oven to roast.
Start-to-Finish
A task can only end when a previous one has started. This is a rare constellation in practice and is particularly suited for handover processes. For example, if you work shifts at a gas station, you cannot finish your work and go home before your colleague who covers the next shift arrives and takes over the task.
For a short project duration, it is favorable if as many tasks as possible can run in parallel. In this case, it is then a matter of available resources how long it takes to complete a project.
Once dependencies are defined, modern project management tools can take this into account when shifting dates. If a task is moved, all dependent tasks are shifted accordingly, unless they have been marked as fixed, immovable tasks beforehand.
Creating a Gantt Chart: Excel or Project Management Software?
Gantt charts are no longer created on paper today but with the help of appropriate software. There are many project managers who are familiar with Excel and use it to create simple Gantt charts. However, a good project management tool offers important features that Excel-based representations and simple tools cannot provide. These include:
- Only flat timeline with limited hierarchy
- Access control only globally at project or file level
- No history and traceability of changes
- Not team-capable, only the project manager can edit the plan
A modern Gantt tool offers these features and should be the standard as soon as projects go beyond small scope.
Alternatives to the Gantt Chart
There are several alternatives to the Gantt chart that can be well-suited for different project management styles and requirements. Here are some of the most common alternatives:
1. Kanban Boards:
- Description: Kanban boards are a visual method for managing tasks, where tasks are divided into columns that indicate progress (e.g. “To Do”, “In Progress”, “Done”).
- Suitability: Ideal for agile projects and teams working in continuous workflows. It is particularly helpful for visualizing workflow and identifying bottlenecks.
- Tools: Allegra, Asana, Jira, Trello.
2. PERT Diagram (Program Evaluation and Review Technique):
- Description: A network diagram that represents tasks as nodes and visualizes their dependencies through arrows. It is used to analyze the scheduling of projects and identify critical paths.
- Suitability: Useful for very complex projects with many dependencies and uncertain time estimates. It enables more accurate planning when there are uncertainties about task durations.
- Tools: Microsoft Project, Lucidchart.
3. Network Planning Technique (Critical Path Method, CPM):
- Description: Similar to the PERT diagram, the network planning technique focuses on the critical tasks in the project that directly affect project completion.
- Suitability: For projects where critical paths and dependencies are the primary focus. It helps identify tasks that must be completed on time to avoid delays.
- Tools: ProjectLibre, GanttProject.
4. Roadmaps:
- Description: A high-level representation of a project’s key phases, milestones, and goals. It does not show detailed tasks but rather long-term goals and time frames.
- Suitability: Ideal for strategic planning and for stakeholders who need an overview of important milestones and goals.
- Tools: Aha!, Monday.com, Roadmunk.
5. Burndown Charts:
- Description: A chart that shows the remaining workload compared to the remaining time. It shows how much work is left and whether the team is on track.
- Suitability: Perfect for agile projects, especially in Scrum teams. It helps monitor progress within a sprint or iteration.
- Tools: Allegra, Easy Agile, Jira, ScrumDo.
6. Task Lists (To-Do Lists):
- Description: Simple lists of tasks that need to be completed. They provide a clear, unstructured overview of what needs to be done.
- Suitability: Ideal for smaller projects or personal task management, where no complex dependencies or detailed schedules are required.
- Tools: Todoist, Microsoft To Do, Wunderlist.
7. Mind Maps:
- Description: A visual representation of ideas, tasks, and concepts that branch out from the main topic.
- Suitability: Useful for brainstorming sessions and for organizing thoughts in the early planning phase of a project.
- Tools: XMind, MindMeister, Coggle.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Gantt chart explained simply?
A Gantt chart is a visual representation of a project’s schedule, where tasks are displayed as bars on a timeline. It shows the start and end of each task as well as its duration and overlaps, making it easy to identify project phases and dependencies.
How do I create a Gantt chart?
You can create a Gantt chart in 6 steps: 1. Define the project and its tasks. 2. Determine the timeline and work duration for each task. 3. Assign resources. 4. Create the time bars in the chart. 5. Adjust the order and overlaps. 6. Monitor and update the chart regularly.
How do I create a Gantt chart in Excel?
To create a Gantt chart in Excel, open a new Excel worksheet, enter your project information, and convert it into a bar chart. Adjust the bars to reflect start and end dates, and format the timeline for a clear presentation. This way you effectively visualize project schedules.
What does a Gantt chart look like?
A Gantt chart is a visual representation of project schedules, consisting of a vertical list of project activities, a horizontal timeline, and bars representing the duration and status of each activity. Arrows indicate dependencies between tasks, which helps with project planning and monitoring.

Christoph Friedrich
CEO Alltena GmbH
Christoph Friedrich is a computer scientist and certified Project Management Professional. He has extensive experience in the introduction and integration of project management tools as well as the analysis and definition of processes in project and service management.



