A Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is the foundation of effective project planning. In this article, I will explain with a WBS example the various methodological approaches available and how to quickly develop a solid plan.
What needs to be done?
A project plan must answer the following four questions:
- WHAT needs to be done?
- WHO is responsible?
- WHEN does it need to be done?
- HOW MUCH effort is required?
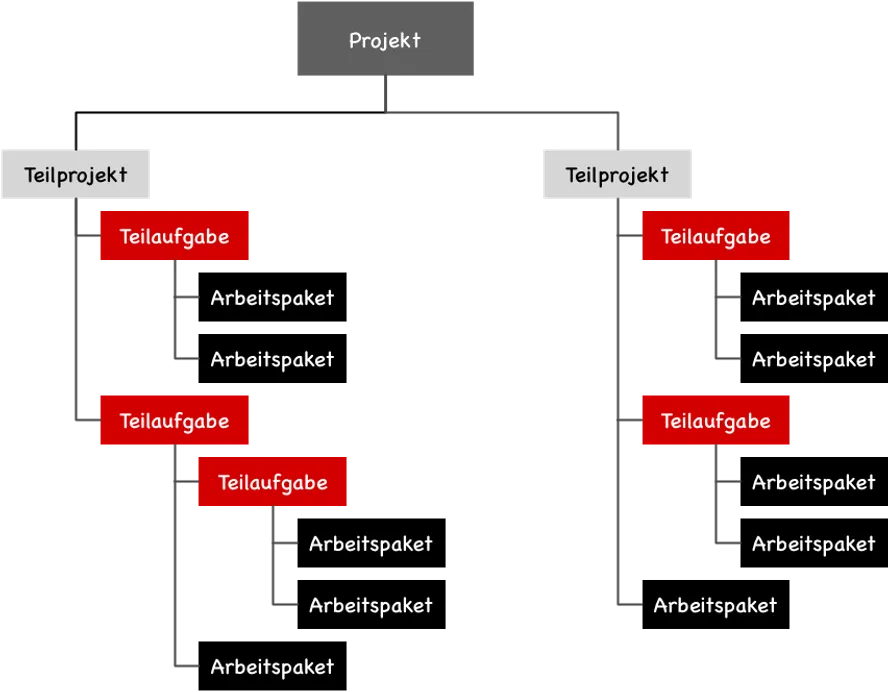
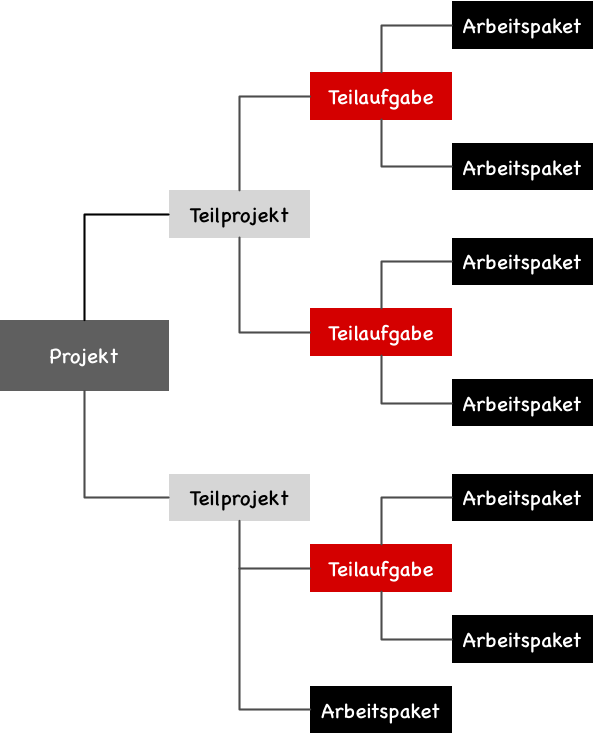
A Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) roughly answers the “WHAT” question with a structured collection of activities or deliverables. Depending on the methodology, this structuring of a project into individual elements is called a Project Breakdown Structure (DIN 69901-5), Product Breakdown Structure (PRINCE2), or Work Breakdown Structure (PMBOK® Guide 2017).
All of these plans include all elements of a project and their relationships to each other. The elements are hierarchically arranged in a tree structure, without specifying the exact timing of their execution.
Based on this “plan of plans,” the subsequent planning stages address scheduling, resource planning, and cost planning.
The structure of a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) according to DIN69901-5 involves three types of elements:
- Subprojects
- Subtasks
- Work Packages
Subprojects allow the use of different process models within an overall project. For example, it might be useful to use a traditional waterfall method for the development of electronics in a subproject and agile methods for the associated software development in another subproject.
Subtasks are elements that can be further broken down in the WBS.
Work Packages represent the lowest level of a WBS and can be further divided into activities or tasks in the planning process.
In this form, the WBS appears activity-oriented, focusing on activities rather than results. A Product Breakdown Structure emphasizes deliverables, while a Work Breakdown Structure requires a combination of activities and verifiable outcomes.
What are the Advantages of a WBS?
The Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is the “plan of plans,” the foundation for all further planning. It offers, among other things:
- A structure for all project management activities
- A complete representation of the scope of work
- Projects with a clear definition of the project goal
- Identification of all work packages belonging to the project
- Creation of a basis for a cost breakdown structure
- Transparency for all project stakeholders
- Provision of a nomenclature for all project documents
- Better planning of dependencies
- Easier scheduling
- Simpler resource planning
- Projects with better cost control
Finding Elements
To create a Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) or Product Breakdown Structure (PBS), I first need to identify the relevant elements in the associated projects. I envision two key points in time: the starting situation and the end situation. If the end situation can be described by objects that are to be created during the project, I break these objects down into sub-objects. If the sub-objects are not purchasable or primitive, I further break them down. This way, I create the plan in a product-oriented manner.
If the projects are highly activity-oriented, such as a move, I collect the activities and try to categorize them. For example, in a move, the rooms can serve as the top-level categories.
Collecting the elements for the project or subproject can be supported by mind mapping or brainstorming.
Organizing Elements in Your WBS
How do I arrange the elements for my structure plan? For the project structure plan, there are three suggestions according to DIN 69901, depending on the type of project, to achieve a good structure:
- Object-oriented structure
- Function-oriented structure
- Time-oriented structure
In the following, we will go through these principles using a small example, the construction of a small workshop.
Object-oriented structure
This approach is best when the project goal is a specific object, such as a garage, an office building, or a gas burner. The object-oriented structure results in a plan that is very similar to a product structure plan according to PRINCE2.
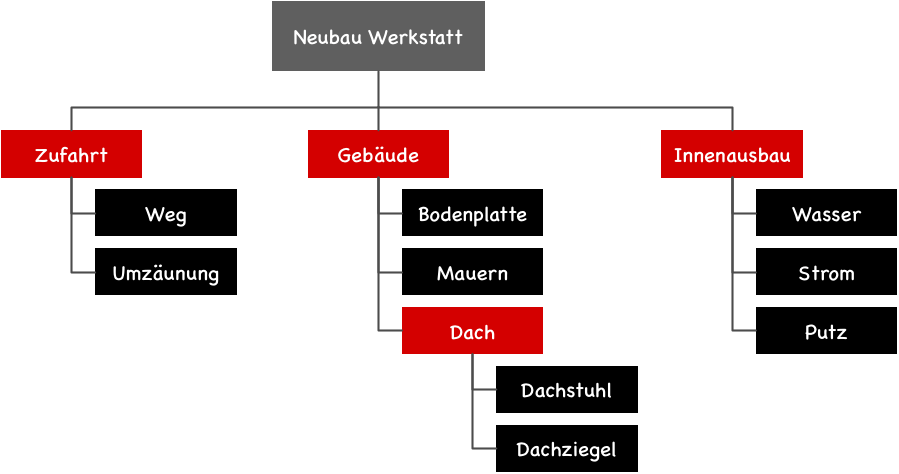
The advantage over a function-oriented approach lies in better traceability during project execution. An outcome is easier to verify than activities. Process verification requires real-time project monitoring, whereas verification based on process results can be done much later without any issues.
An object-oriented project structure plan is essentially a product structure plan if you include not only the final products but also intermediate products such as design documents or test reports.
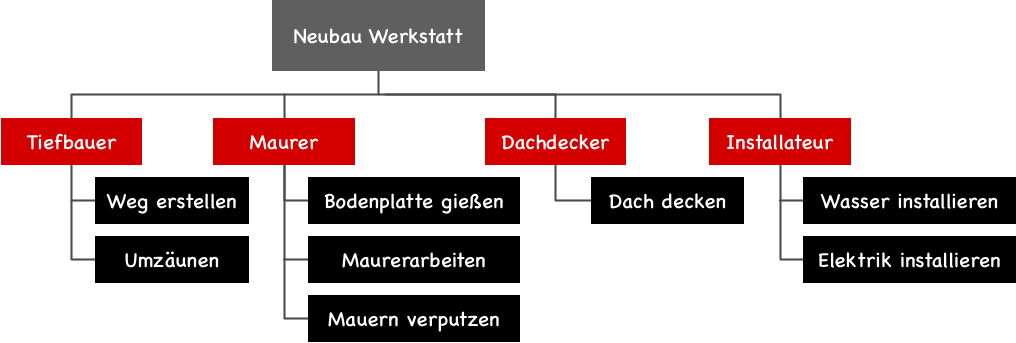
Function-oriented structure
The function-oriented structure is best when the project can be more clearly described by the activities or work packages to be carried out rather than by the results of the activities. For example, while I could describe the outcome for a move, I would miss the essential aspect, which is the relocation of items from the starting point to the destination.
For comparison, I have created a function-oriented project structure plan for building a garage in the next illustration. Unlike a move, in this case, a function-oriented approach is also possible.
Time-oriented structure
In a time-oriented structure, I create the plan directly from the necessary tasks. I think about the sequence of the project, i.e., what needs to be done one after the other. I write these activities on a list or enter them into a suitable project management tool. If the list gets longer, I structure the sequence into phases. For a move, for example, I would foresee a phase for each room and then phases for furniture and small items.
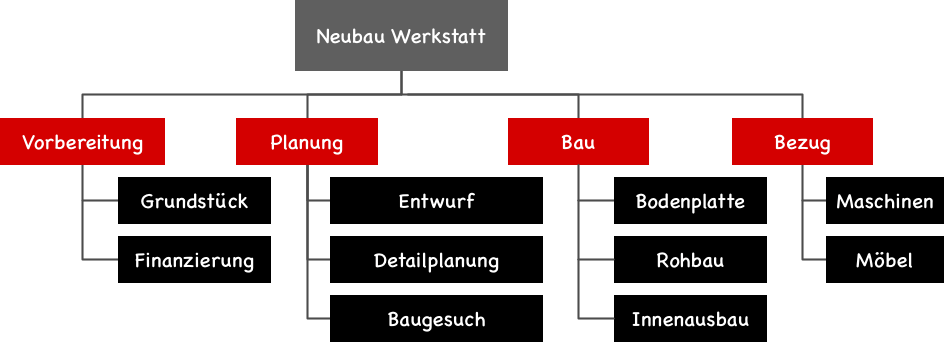
Which structuring principle to apply?
I choose the structuring principle based on the type of project if I have the freedom to do so. I prefer the object-oriented approach whenever possible and only use the function-oriented methodology when it doesn’t fit. The function-oriented structure is suitable for projects where the project can be more clearly described by its activities than by the results of the activities.
Coding Elements in your WBS
To uniquely identify the individual elements in the project structure plan, it is important that they receive a code. This ensures that efforts, resources, or changes can always be clearly assigned to a work package later. The coding must reflect the hierarchical position of the element. Different types of coding are distinguished:
- Numeric Coding: Use of digits, e.g., 1, 1.1, 1.1.2…
- Alphabetic Coding: Use of letters, e.g., A, AA, AB, …
- Alphanumeric Coding: Combination of numbers and letters, e.g., A, A1, A.1.1 …
- Dewey Decimal Coding: Digits in a decimal format, e.g., 1000, 1100, 1110 …
How detailed should I plan?
A major challenge in creating a work breakdown structure (WBS) is finding the right level of detail. It would be unwise to plan steps early in the project that depend on many conditions and where it is not foreseeable how these conditions will look at the time of the plan’s execution.
The golden rule for WBS is:
A WBS should always fit on one sheet!
A WBS should not contain more than 50 elements.
A small project fits on a DIN A4 sheet, a large one may require a DIN A2 sheet.
Tips
Know Requirements and Scope
At the very least, the project manager should have a rough understanding of the project goal or deliverable before creating a work breakdown structure (WBS). It is very helpful if a requirements specification has already been created at this stage. Working out the requirements is best done in its own project or in a pre-project phase.
Create the Plan as a Team
A reliable work breakdown structure should be developed as a team. An individual can easily overlook important elements, which can have a negative impact over the course of the project. It is also beneficial for team building and project identification to involve participants early in the project.
Sleep on It
A work breakdown structure should, if possible, not be completed in one go, but rather be allowed to rest like a dough before further processing. After a break of a few days, you can review your work with a proper distance and correct it if necessary.
The 7 by 7 Rule
The week has 7 days, and hands have ten fingers. This is not a coincidence. Therefore, arrange a maximum of 7 to 10 elements on the first level of structure and similarly a maximum of 7 to 10 elements on the second level. There should be no more than 50 elements in total. A high level of detail is detrimental to clarity and increases the workload.
Planable and Controllable
The work breakdown structure should be detailed enough so that the resulting work packages and subtasks are planable and controllable. Many projects fail because the work packages were defined too broadly in the planning phase.
The WBS Must Fit on One Page
Bringing clarity to the project or subproject with its many tasks is an important purpose of the work breakdown structure. Therefore, it should not be spread over many pages but should be able to be presented on one page.
Put the WBS on the Wall
Print the work breakdown structure on a large sheet and hang it in a prominent place on the wall. This makes it a central communication tool in the project and focuses the team on the important points of the project.
Tools
The Sticky Note Wall
Writing cards and pinning them to a board is a proven approach, especially in the early planning phase. This makes the plan simple to create. This way, the entire team can be involved, and reordering and structuring is very easy.
Special WBS Tools
There are not many tools specifically dedicated to creating work breakdown structures (WBS). Most project management software does not offer this function as such. This is probably because this task can be almost equally well handled by modern diagram tools or because the structuring can be done directly in the form of a Gantt chart.
Diagram Tools
Diagram tools like Visio or OmniGraffle allow for the quick and easy graphical creation of tree structures, which WBS essentially are. These tools even offer automatic layout functions and the ability to define custom shapes, allowing WBS codes to be uniformly formatted within the elements.
Mind Mapping Tools
The central function of mind mapping is to outline a project and its corresponding plan into hierarchically arranged elements. Therefore, tools like MindManager or MindGenius are particularly suitable for the collection phase.
Anita Coltuneac
Author