Summary: Project management deals with the planning, execution, and monitoring of projects. There are two main approaches: Traditional project management with sequential planning and agile project management with flexible, iterative processes. Within these approaches, there are various models such as the Waterfall model and Scrum, each offering specific techniques and processes. Overarching reference models like CMMI and ISO 9001 define quality criteria for good project management.
What is Project Management?
A project is a time-limited endeavor for which a specific effort is planned in order to achieve a clearly defined goal. The term comes from the Latin “projectus,” meaning “thrown forward,” underscoring the forward-looking nature of planning. Projects are carried out by project teams whose tasks and collaboration must be coordinated. This is precisely what project management is for.
History of Project Management
The roots of project management reach back to antiquity, when complex construction projects such as the pyramids in Egypt, the aqueducts in Rome, and the Great Wall of China required extensive planning and organization. In the 20th century, modern project management began to develop as a distinct discipline, particularly driven by the Industrial Revolution, which brought new complexity to manufacturing and construction. A significant advancement was the introduction of Gantt charts in the 1910s, which made it possible to visually represent project plans and better track tasks.
In the 1950s, large infrastructure projects such as the construction of highways and dams in the United States drove the development of new techniques like the Critical Path Method (CPM) and the Program Evaluation and Review Technique (PERT). These methods revolutionized how projects were planned and monitored by identifying dependencies and using resources more efficiently.

With advancing digitalization and globalization, project management has evolved further over recent decades. Agile methods like Scrum and Kanban gained importance, particularly in software development, complementing traditional project management. Today, project management is a central discipline in nearly every industry, enabling the effective planning, execution, and completion of complex projects. Project execution is simplified by project management software. Many organizations run multiple projects in parallel. Coordinating them is aided by project portfolio management.
Project Lifecycle and Project Phases
Every project goes through a project lifecycle from the initial project idea to the completion of all project activities, which is divided into project phases. Which project phases exist depends heavily on the industry and the type of project.
A commonly used project lifecycle consists of four project phases:
| Phase | Activities and Deliverables |
|---|---|
| 1: Preparation |
|
| 2: Planning |
|
| 3: Execution |
|
| 4: Closure |
|
The 10 Knowledge Areas of Project Management
One of the most significant project management standards, the PMBOK, divides project management into 10 knowledge areas. Not all aspects are equally relevant for every project, and this model can be adapted to your own needs.
| Knowledge Area | Core Processes (Excerpt) |
|---|---|
| 1: Integration Management |
|
| 2: Scope Management |
|
| 3: Schedule Management |
|
| 4: Cost Management |
|
| 5: Quality Management |
|
| 6: Resource Management |
|
| 7: Communications Management |
|
| 8: Risk Management |
|
| 9: Procurement Management |
|
| 10: Stakeholder Management |
|
Integration Management is a key area in the PMBOK Guide and emphasizes the coordination of all project aspects. It ensures that processes and activities are aligned with project objectives and that resources are used efficiently.
Scope Management ensures that a project includes only the work necessary to be completed successfully by defining what is and is not included in the project.
Schedule Management aims to complete the project within the established time frame by creating a realistic schedule aligned with objectives and resources.
Cost Management focuses on planning, budgeting, and controlling costs to ensure the project stays within the approved budget.
Quality Management ensures the project meets established requirements and standards to secure customer satisfaction.
Resource Management deals with the efficient planning and management of all resources needed for the project, such as personnel and materials.
Communications Management encompasses the planning and execution of all communication processes to ensure the project’s information needs are met.
Risk Management identifies, assesses, and controls risks to minimize the impact of unexpected events.
Procurement Management handles the acquisition of goods and services from external suppliers required for the project.
Stakeholder Management aims to consider the interests of project participants and meet their expectations.
The Most Common Methods
Project management methods are structured approaches for planning, executing, monitoring, and closing projects. Project management methods provide specific techniques and processes designed to help execute projects efficiently and effectively.
There are two major schools of thought, each advocating a different fundamental approach to project management. These methods are:
- Traditional project management with thorough planning and a sequential approach
- Agile methodology with flexible planning and an iterative approach
Within these schools, there are a number of differently designed process models. For the traditional methodology, these include primarily the Waterfall Model, the V-Model, PRINCE2, the Spiral Model, and the Rational Unified Process. For the agile school, these include primarily Scrum, Kanban, DevOps, and Extreme Programming.
Above all of these are the reference models that provide criteria for the quality of specific process implementations and thus imply what constitutes good project management. The best-known reference models are CMMI, ISO/IEC 15504, ISO 9001, and Automotive SPICE.
Traditional Project Management Methods
Traditional project management methods follow a comprehensive and holistic approach. At the start of the project, a clearly defined end state is established and planned. Costs, schedules, resources, quality, and benefits are considered from the beginning.
The best-known traditional project management method is the Waterfall Model, which is why it is often used as a synonym for traditional project management. The original V-Model is an evolution of the Waterfall Model. The highly useful V-Model XT (development standard) extends the generic V-Model. The Spiral Model and IBM’s Rational Unified Process (RUP) can also be classified as traditional project management methods.
Waterfall Method
The Waterfall Model is a project management approach that has been used for decades. It is a linear and sequential method where the project is divided into phases. Each phase must be completed before the next one can begin. Phases include requirements gathering, design, implementation, testing, and deployment.
V-Model XT
The term “V-Model” refers both to a general process model designed for software development and to a development standard. The latest version of this standard is called V-Model XT and supports not only the approach of the general process model but also many other approaches.
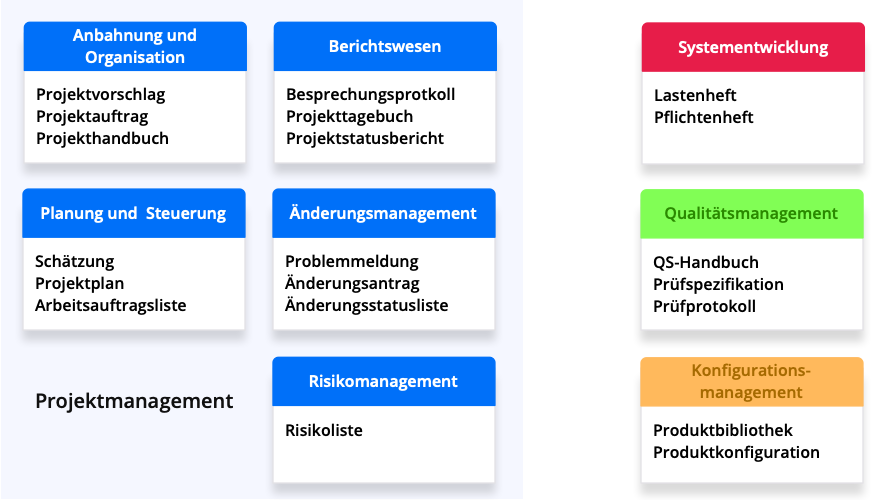
This standard is a framework for Systems Engineering and project management. It is an extension and specification of the Waterfall Model and is often applied in safety-critical and complex projects.
The V-Model XT proposes a concrete approach. To this end, all necessary activities with their respective results—the “deliverables”—are named and defined. For many deliverables, templates are available that can be used directly.
Critical Chain Project Management
Critical Chain Project Management (CCPM) prioritizes work packages and minimizes multitasking and project duration through buffer management. The approach is as follows:
- Identify critical resources: First, resources that could cause bottlenecks are identified.
- Create the Critical Chain: After identification, tasks that require these resources and form the longest path are combined into the Critical Chain.
- Estimation and buffer management: Estimates are created with a 50% probability, and the difference to conservative estimates serves as a buffer for all tasks on the Critical Chain.
- Operational prioritization: Tasks on the Critical Chain are preferentially worked on based on progress and buffer consumption.
- Ongoing monitoring and adjustment: Progress is continuously monitored and adjusted as needed to ensure on-time completion.
CCPM accounts for buffers in estimates to minimize delays and optimize project duration.
Agile Project Management Methods
Agile project management divides projects into small, easily plannable units called iterations or sprints. During each iteration, a portion of the project is developed, tested, and evaluated. The most important agile methods are Scrum, Kanban, and Extreme Programming (XP).
Agile approaches have gained significantly in popularity in recent years and are applied across various industries, from software development to product management and marketing.
Scrum
Scrum is an agile project management method primarily used in software development to manage complex projects efficiently and flexibly. It is usually supported by specialized project management tools and is based on an iterative and incremental approach that enables teams to deliver functional product increments in short cycles called sprints. These sprints typically last two to four weeks and each ends with a potentially shippable product increment.
A Scrum team consists of three main roles: the Product Owner, the Scrum Master, and the Development Team. The Product Owner manages the Product Backlog, a prioritized list of requirements and tasks, and ensures that the team works on the most valuable items. The Scrum Master supports the team in applying the Scrum process and removes impediments that could hinder progress. The Development Team, which is self-organizing, is responsible for implementing and delivering the tasks.
Each sprint begins with Sprint Planning, where the team selects the tasks for the upcoming sprint. During the sprint, the team meets daily for a brief Daily Scrum to discuss progress and identify any impediments. At the end of each sprint, a Sprint Review takes place where the team presents the product increment and gathers feedback. The team then reflects on the work process in the Sprint Retrospective and identifies opportunities for improvement.
Through these regular iterations, Scrum promotes transparency, continuous improvement, and close team collaboration, enabling projects to be executed efficiently and flexibly.
Kanban
Kanban is an agile method for optimizing workflows, originally developed in manufacturing and now used across many industries, particularly in software development. Kanban’s primary focus is on visualizing the workflow and continuous improvement.
The method uses a Kanban board on which tasks are visualized as cards and moved through various columns representing different phases of a process. Typical columns include “To Do,” “In Progress,” and “Done.” This enables teams to see the current status of each task at a glance and quickly identify bottlenecks.
A central element of Kanban is limiting work in progress (WIP). This limit prevents overload and maintains focus on completing tasks.
Kanban promotes continuous improvement through regular review of the workflow and process adjustments to increase efficiency. Since Kanban is flexible and does not use fixed iterations like Scrum, it is particularly well suited for teams working in dynamic environments that require constant adaptation of their work methods.
Scrumban
Scrumban is a hybrid project management method that combines elements of Scrum and Kanban to merge the flexibility of Kanban with the structure of Scrum. This method is particularly well suited for teams working in dynamic environments that want to leverage both the iterative planning of Scrum and the continuous improvement of Kanban.
In Scrumban, tasks are displayed on a visual board showing the workflow, similar to Kanban. Tasks are moved through various columns representing different phases of the project. The number of tasks in progress (Work in Progress, WIP) is limited to prevent overload and maintain focus on completion.
Scrumban retains Scrum elements like sprints, daily standups, and retrospectives to ensure regular review of progress and team dynamics. At the same time, it allows the flexibility of Kanban to respond to changes in prioritization and work requirements without being bound to fixed sprint cycles.
By combining Scrum and Kanban, Scrumban offers an adaptable structure that promotes both efficiency and agility. This method is particularly well suited for teams striving for incremental improvements while continuing to deliver regularly and respond to changes.
DevOps
DevOps is a methodology that unites Development and Operations in software development to improve the efficiency, quality, and speed of software delivery. It aims to foster collaboration between developers and operations teams, thereby breaking down the silos that traditionally exist between these departments.
A central aspect of DevOps is the automation of the software development process, including testing, deployment, and monitoring. By automating repetitive tasks, error susceptibility is reduced and lead times from code development to production are shortened. Continuous Integration (CI) and Continuous Delivery (CD) are important DevOps practices that enable code to be continuously integrated into a shared codebase and quickly moved to production.
DevOps also emphasizes the importance of continuous feedback and monitoring to ensure software performance and stability. This fosters a culture of continuous improvement where teams can quickly respond to problems and implement solutions.
Overall, DevOps enables faster, more reliable, and more efficient software delivery, making it easier for organizations to respond to changing market conditions and customer requirements while ensuring software quality and stability.
Supporting Methods
A number of methods cover only a very specific aspect of project management or are collections of terminology, principles, and practices like the PMBOK. Others primarily fall into the “time management” or “productivity” category. We therefore do not list them here as project management methods, but only as “supporting methods.” They are mostly used as supplements to the more comprehensive methods.
Earned Value Method
The Earned Value Method (EVM) is a project management technique used to measure project progress and performance. It compares a project’s planned progress with the actual progress achieved and the costs incurred. EVM uses three key metrics: Planned Value (PV), Earned Value (EV), and Actual Costs (AC).
Planned Value (PV) indicates what was planned at a given point in time, while Earned Value (EV) represents the actual value of work performed. Actual Costs (AC) are the actual costs for the work delivered.
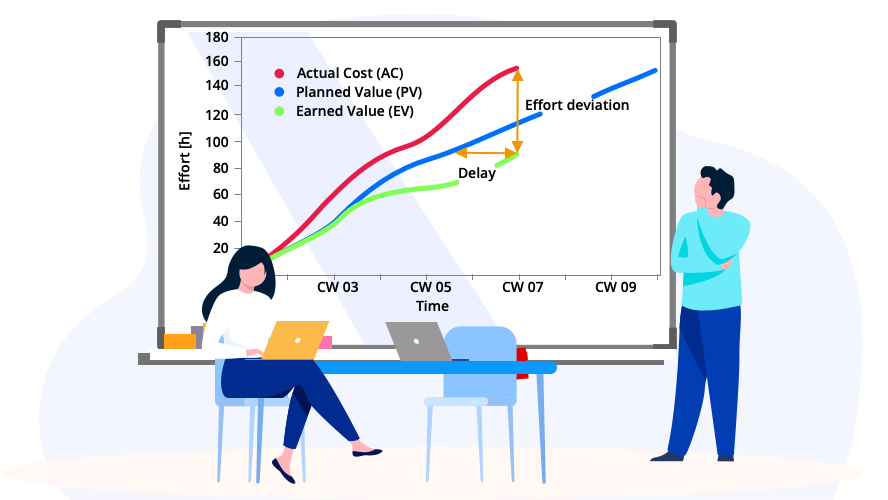
By calculating variances between these values, such as the Cost Performance Index (CPI) and Schedule Performance Index (SPI), project managers can monitor the financial and schedule status of the project, identify trends, and take early corrective action. The better project management tools support this method.
Network Planning Technique
The Network Planning Technique is a project management method for planning, controlling, and monitoring projects. It enables the representation of processes or activities, their dependencies, and the timeline in a network diagram. Two main approaches are used in network planning: the Activity-on-Node (PERT) and the Activity-on-Arrow (CPM) approach.
In the PERT approach, activities are represented as nodes connected in a diagram. Each activity has an estimated duration and a probability of being completed within that duration. PERT enables the calculation of the most likely project duration and the identification of critical paths.
In the CPM approach, activities are represented as arrows connecting events such as milestones. CPM uses fixed durations for activities and focuses on identifying the critical path to determine the earliest possible project completion date.
Both approaches enable detailed planning, resource allocation, and time management to achieve project goals on schedule and identify bottlenecks. The network planning technique is particularly useful for complex projects with many activities and dependencies.
Milestone Trend Analysis
Milestone Trend Analysis (MTA) is a project management technique that tracks a project’s progress using milestones. It compares planned milestone progress with actual progress and identifies deviations.
For visualization, milestone dates are plotted on the Y-axis at the project start. The dates of planned project status meetings are marked on the X-axis. At each status meeting, milestone dates are updated and entered into the chart. If milestones move upward over time, this indicates a delay. If milestones remain on a horizontal line, the project is on schedule.
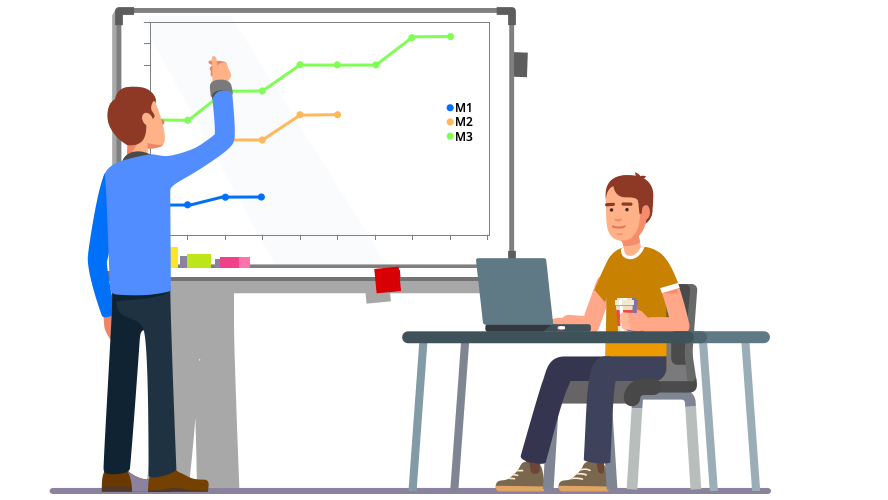
Through MTA, project managers can detect potential problems early and take corrective action to get the project back on track. This method provides insights into a project’s schedule and financial status and enables proactive response to delays or deviations.
Six Sigma
Six Sigma is a data-driven method for process improvement that aims to minimize defects and deviations in business processes. The method uses statistical analysis to identify the root causes of problems and systematically eliminate them to achieve high quality and efficiency.
Six Sigma follows the DMAIC cycle, consisting of five phases: Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control. In the Define phase, goals and problem statements are defined. Measure involves collecting and analyzing data to understand the current state. In the Analyze phase, root causes of problems are identified. Improve focuses on developing and implementing solutions, while the Control phase involves taking measures to sustain the improvements permanently.
Six Sigma aims to reduce process variability and achieve near-defect-free production, resulting in cost savings and higher customer satisfaction.
Key Components and Concepts in Project Management
The following is a list of important project management concepts.
| Concept | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Magic Triangle | The magic triangle in project management describes the three central success factors of a project: time, cost, and quality. These factors are interdependent, so changes to one element affect the others. |
| Milestone | A milestone is an important event or checkpoint in a project that marks progress. It serves as a control point to ensure the project stays within its time and budget framework. |
| Project Scope | The project scope defines all work and tasks required to achieve the project objectives. It determines what is included in the project and what is not, setting clear boundaries for the work. |
| SMART Goals | SMART goals are Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Realistic, and Time-bound goals used in project management to define clear and actionable targets. This project management method helps to purposefully steer and verify a project's success. |
| Timeline | A timeline is a visual plan that represents the chronological sequence of tasks and milestones within a project. It helps track progress and ensure the project is completed on schedule. |
| Work Breakdown Structure | The Work Breakdown Structure (WBS) is a hierarchical decomposition of project tasks that breaks down the entire project into manageable units. It serves as the basis for planning, resource allocation, and control. |
| Roles | A role in project management describes the specific responsibilities and tasks of a person or team within the project. Clear role assignments provide structure and accountability in the project. |
| Milestone | A milestone is an important event or checkpoint in a project that marks progress. It serves as a control point to ensure the project stays within its time and budget framework. |
| Budget | The budget in project management encompasses the financial resources allocated for carrying out a project. It covers all expenses, including personnel, materials, and other costs, to achieve the project objective. |
| Dependencies | Dependencies in project management describe the relationship between tasks where one task can only begin or be completed once another task is finished. They significantly impact the project schedule, as delays in one task can affect subsequent tasks. |
How Do I Become a Project Manager?
There are many paths to becoming a project manager. Typically, you first complete training—depending on the industry, either vocational training or an academic education. Then you work on projects for some time. At some point, one of your supervisors notices you and proposes you as a project leader. Until now, you were a technically skilled specialist. Now you’re suddenly expected to be proficient in project management. Here is one of many possible approaches:
- Get a copy of the PMBOK
- Download a copy of the V-Model XT
- If possible, complete a recognized project management certification
- Use good project management software like Allegra
- Create your own project manual from a project manual template
- Follow the approach you’ve established in your project manual
If you also:
- Communicate well
- Involve your team in project management
- Trust your team
- Document everything thoroughly
then nothing stands in the way of your success!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is project management?
Project management deals with the planning, execution, and monitoring of projects, distinguishing between two main approaches: traditional project management with sequential planning and agile methodology with flexible, iterative processes.
What is project management and what methods are there?
Project management deals with the planning, execution, and monitoring of projects. There is traditional project management with sequential planning and agile methodology with flexible, iterative processes. Within these approaches, there are various models such as the Waterfall Model and Scrum, each offering specific techniques and processes. Overarching reference models like CMMI and ISO 9001 define quality criteria for good project management.
How do I become a project manager?
There are many paths to becoming a project manager. To be successful, you need a) industry knowledge, b) leadership skills, and c) project management expertise. Industry knowledge is acquired through a degree or vocational training and several years of work experience in an industry. Leadership skills are either innate or developed through appropriate courses. Project management expertise is best acquired by preparing for a corresponding certification.

Jörg Friedrich
Senior Advisor
Jörg Friedrich is the original author of the project management software Allegra and continues to accompany its development to this day. He has many years of industry experience as a project and department manager. He also serves as a professor in the Faculty of Computer Science and Information Technology at Esslingen University of Applied Sciences.




